Let’s start with the basics of hearing loss and the different types of hearing loss.
Nowadays, when we look around, we often see people using earphones while traveling—on the train, the bus, and elsewhere. This habit poses a serious risk of hearing loss in the future due to consistently listening at high volumes. If this continues, the number of people experiencing hearing loss is expected to increase. Hearing impairment or deafness is considered a form of disability and is the second most common disability after mobility impairment. It is a hidden condition that can be difficult to detect—even for the person affected. Without conversation, we might not even realize that someone has hearing difficulties. In this article, we will explore the types, causes, treatments, and mechanisms of human hearing.

Types of Hearing Loss
Conductive Hearing Loss
Causes: Damage to the middle ear or blockage in the outer or middle ear, such as earwax, fluid, infection, or tumors. It can also result from congenital conditions like ear canal atresia or underdeveloped outer ears.
Treatment: There are several treatment options for conductive hearing loss, including non-surgical options such as bone conduction hearing devices.
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Causes: Damage or loss of the hair cells in the cochlea, or prolonged exposure to loud noise. Sensorineural hearing loss is also commonly associated with aging as part of the natural degeneration process.
Treatment: Treatment options vary depending on severity and may include cochlear implants, middle ear implants, electro-acoustic stimulation, or wearing hearing aids.
Mixed Hearing Loss
Causes: A combination of sensorineural and conductive hearing loss, caused by problems in both the inner ear and the outer or middle ear.
Treatment: Treatment options for mixed hearing loss include middle ear implants and bone conduction cochlear implants.
Next, let’s take a look at how our ears process sound in five simple steps — easy to understand and not complicated at all.
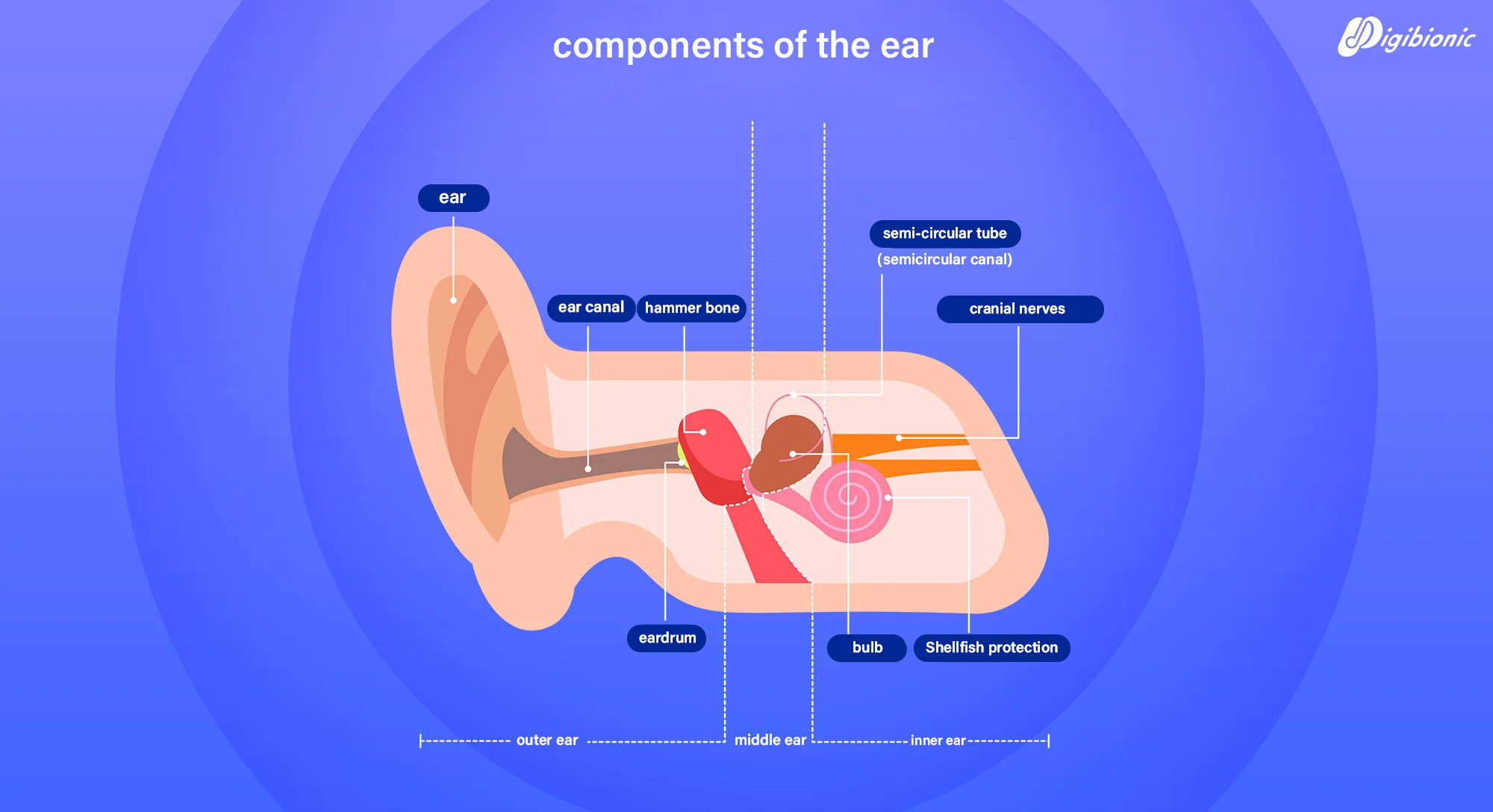
How Do Our Ears Work?
Step 1 Sound first enters through the outer ear, which collects and channels it into the ear canal. This causes the eardrum to vibrate.
Step 2. The vibration of the eardrum sets the three tiny bones in the middle ear into motion.
Step 3. As the sound passes through these bones into the inner ear, it stimulates the hair cells, causing them to vibrate.
Step 4. The sound signals are then transmitted to the auditory nerve.
Step 5. The auditory system sends these sound signals to the brain, where they are analyzed and perceived as sound.
After understanding how our hearing system works, it becomes clear that even minor damage to any part of the ear can lead to hearing loss — because every component must work together in harmony.
Next, we’ll explore the three most common types of hearing loss and the impacts they can have.
1. Conductive Hearing Loss
Conductive hearing loss occurs due to injury or blockage in the outer or middle ear that prevents sound from being transmitted properly. Common causes include middle ear infections, earwax blockage, and perforated eardrums. Fortunately, this type of hearing loss can often be improved and restored with proper rest and continuous treatment.
2. Sensorineural Hearing Loss
This type of hearing loss is mainly caused by damage to the inner ear or auditory nerve, often due to aging, exposure to loud environments, or bacterial infections. Sensorineural hearing loss usually progresses gradually, so many people are unaware of it until it reaches a moderate to severe level.
3. Mixed Hearing Loss
Mixed hearing loss combines the two types above. For example, someone may experience middle ear damage from infection or perforation and, over time, be exposed to prolonged loud noise, leading to both conductive and sensorineural hearing loss.
4. Impacts of Hearing Loss
Hearing loss is closely related to daily life. Individuals with hearing loss often report higher incidences of other health issues, such as falls, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and Alzheimer’s. It also affects communication, leading to misunderstandings and social withdrawal. Hearing loss can negatively impact interpersonal relationships and cognitive function over time.
Read more: Linking hearing loss to various medical conditions.
5. Coping with Hearing Loss
Medical Treatment: For conductive hearing loss, prompt treatment with medication or surgery can restore hearing. If you notice difficulty hearing conversations or unusually low environmental sounds, consult a doctor immediately.
Wearing Hearing Aids: For hearing loss that cannot be medically treated, hearing aids are the primary solution. Modern high-tech hearing aids can be customized to the user’s specific hearing loss, reduce background noise, and distinguish between human and non-human sounds. While highly effective, they often require individual adaptation.
Environmental Considerations: Even advanced hearing aids may have limitations in noisy environments.
Family Communication: Effective communication is essential. Family members should speak slowly, use lip-reading, and avoid speaking from behind to ensure proper understanding.
In summary, understanding the types and causes of hearing loss is the first step. To prevent premature hearing loss, avoid excessive use of headphones or exposure to loud environments. If you or a family member notice early signs of hearing difficulty, seek medical attention promptly to prevent further damage and protect quality of life.

Wearing a hearing aid is the primary solution for hearing loss that is not conductive, as most cases cannot be treated medically. Modern hearing aids have evolved from traditional models to high-tech devices that can be customized to an individual’s specific hearing loss, reduce background noise, and distinguish between human and non-human sounds with high accuracy. Today’s hearing aids can address most hearing problems, although they often require personal adaptation for optimal use.

Hearing Aids: Although hearing aids have advanced significantly, their effectiveness can be limited in certain environments, such as those with high levels of background noise.
Family Communication: Family members should learn proper communication techniques, as communication is essential in daily life. It is recommended that they be patient when interacting with someone with hearing loss, speak slowly, use lip-reading, and avoid speaking from behind. Effective communication with individuals who have hearing difficulties is crucial.
Therefore, once we understand the basics of hearing loss and its types, it is important to take preventive measures to avoid premature hearing problems. This includes limiting the use of headphones at high volumes and avoiding prolonged exposure to loud environments. Additionally, if you notice early signs of hearing loss in yourself or family members, consult a doctor promptly to prevent further damage and protect your future quality of life.
เราใช้คุกกี้เพื่อพัฒนาประสิทธิภาพ และประสบการณ์ที่ดีในการใช้เว็บไซต์ของคุณ คุณสามารถศึกษารายละเอียดได้ที่ นโยบายความเป็นส่วนตัว และสามารถจัดการความเป็นส่วนตัวเองได้ของคุณได้เองโดยคลิกที่ ตั้งค่า