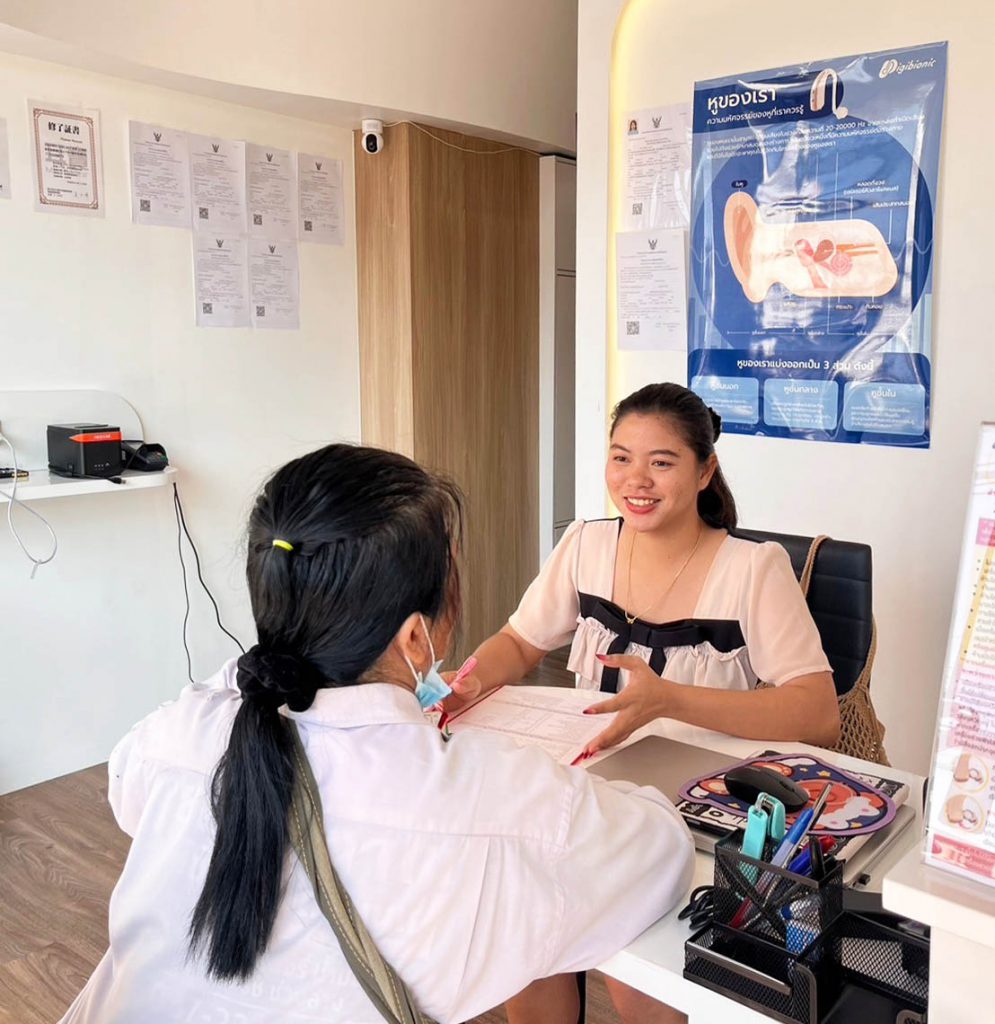
Diagnosis and Assessment of Hearing Loss
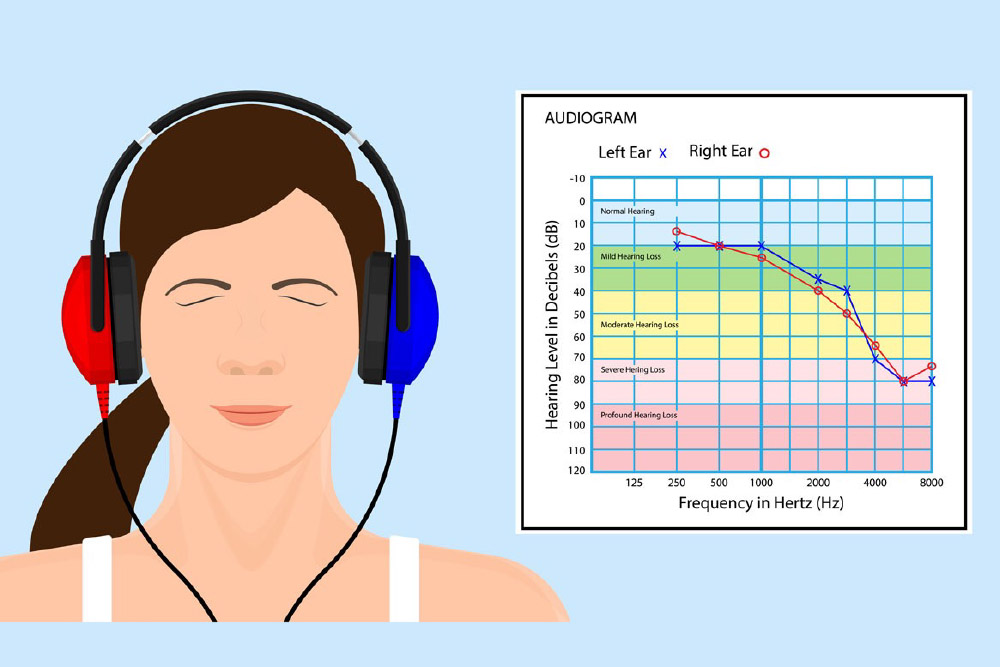
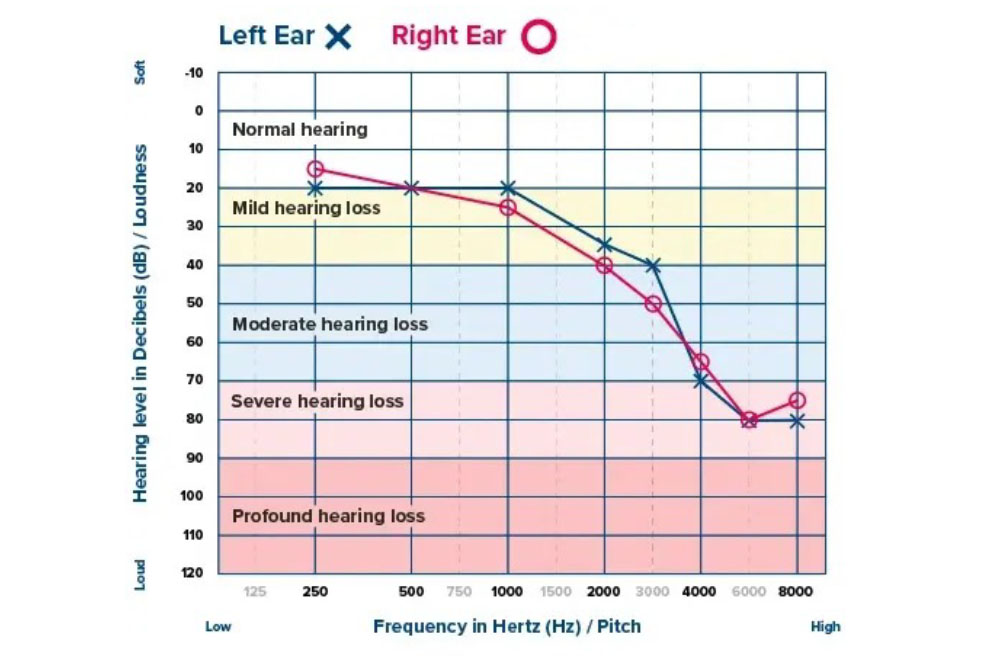
Audiograms help doctors or hearing specialists accurately identify the level and type of hearing loss, which can be classified as mild, moderate, severe, or profound.
Hearing Aid Adjustment
Audiogram results are used to customize hearing aids to match an individual’s hearing profile. The hearing aid is programmed to amplify sounds at the frequencies and levels where the user has hearing difficulties.
Selecting the Appropriate Hearing Device
Audiograms assist in choosing the right type of hearing device, whether it’s a specific hearing aid or supplementary listening devices needed to improve hearing.
Treatment and Therapy Planning
Specialists can use audiogram data to plan treatments or therapies to improve hearing, or to apply techniques that assist with listening and communication in daily life.
Evaluating Treatment or Hearing Aid Effectiveness
Audiograms are used to monitor and assess the effectiveness of therapy or hearing aid use, helping to determine if hearing has improved and to adjust the treatment plan as needed.
Understanding One’s Hearing Condition
Individuals with hearing difficulties can use audiograms to better understand their hearing condition and recognize the importance of preventing further hearing loss.
Daily Life Guidance
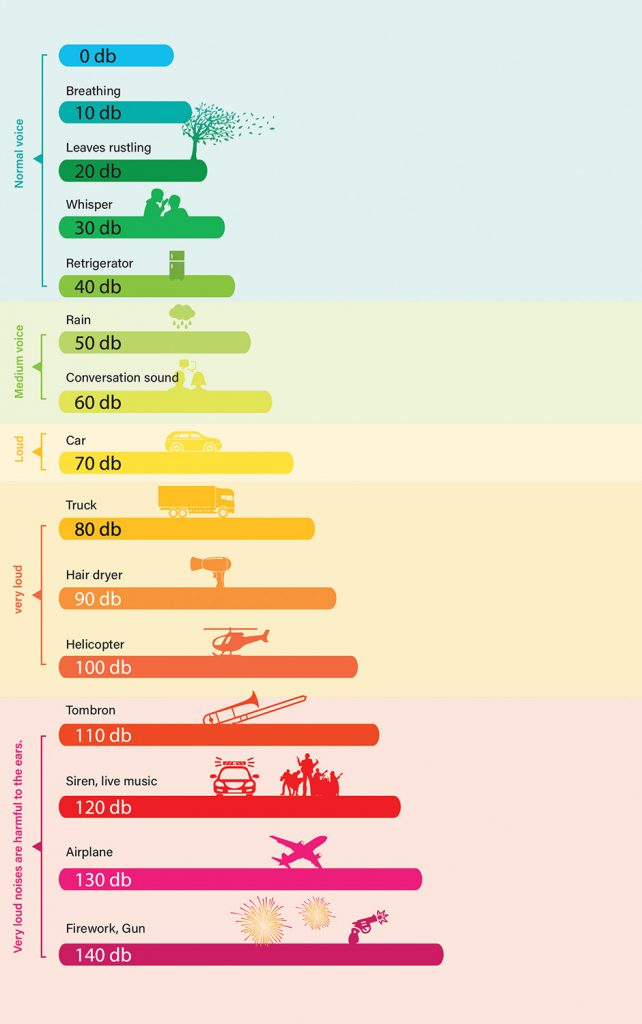
Information from audiograms allows specialists to provide practical advice for daily life, such as choosing suitable places for conversation, using assistive listening technology in different situations, or avoiding excessively loud environments.
Audiograms are a vital tool for managing hearing issues in daily life, providing valuable information for diagnosis, hearing aid customization, treatment planning, and effective guidance for everyday living.